Deep Cycle Maintenance Guide
Table Of Contents [show]
Battery Maintenance Guide & Preventative Maintenance Schedule
Proper battery maintenance or preventative maintenance will help ensure the longest life possible from your batteries. Deep cycle batteries are an expensive expendable component and with a properly executed preventative maintenance you will get the maximum output from them. Most battery failures are operator errors and could have been prevented. We typically see the batteries being overused and under maintained. For instance, not checking the water levels of the cells on a regular basis or using a charger that does not have the proper output for your battery bank. Your maintenance should be performed twice a month at the minimum. The first maintenance should be focused on the visual checking of water levels, battery integrity, damage, loose cables and any tasks that may pertain to your setup. The second maintenance should be cleaning any dirty batteries, spillage, watering and boost charging if needed. Your schedule may change depending on the conditions to the climate in your area. If its colder region, you may be able to reduce your schedule to once a month or every other month. If you live in a warm/hot region your schedule may increase to weekly inspections and maintenance.
Download our Battery Maintenance Log to keep track of your battery maintenance
-
Inspection
- Examine the outside appearance of the battery. The tops of the batteries and terminal connections should be clean, dry, and free of corrosion. Refer to Section 3, Cleaning.
- If fluids are present on the top of a deep-cycle flooded/wet battery, it may mean that the battery is being over-watered or overcharged. Refer to Section 2, Watering, for the proper watering procedure.
- If fluid is present on the top of a deep-cycle AGM or gel battery, it may mean that the battery is being overcharged, which can reduce battery performance and life.
- Check battery cables and connections. Replace any damaged cables and tighten any loose connections. Refer to the Torque Values table below.
-
Watering
- Use only distilled or deionized water. Tap water can contain contaminants that will damage the battery. Also, be aware that water can pick up impurities from containers, piping, and fixtures. The table below contains the limits for impurities to avoid damaging batteries.
- Fully charge the batteries prior to adding water. Only add water to discharged or partially charged batteries if the plates are exposed. In this case, add just enough water to cover the plates and then charge the batteries. Once completed, continue with the watering procedure below.
- Check the electrolyte levels by removing the vent caps and placing them upside down so that dirt does not accumulate on the underside of the cap. For Trojan Plus Series batteries, simply flip open the cap.
- If the electrolyte level is barely covering the plates, add distilled or deionized water to the proper level as illustrated in the images below.
- After adding water, secure vent caps back onto batteries.
-
Cleaning
- For flooded batteries, check that all vent caps are secured properly on the battery.
- Clean the top of the battery, terminals, and connections with a cloth or non-metallic brush, and a solution of baking soda and water comprised of 1 cup of baking soda to 1 gallon of water (60 ml of baking soda per liter of water). Do not allow cleaning solution to get inside the battery.
- Rinse with water and dry with a clean cloth.
- Apply a thin coat of terminal protector spray which can be purchased through your local battery dealer.
- Keep the area around batteries clean and dry
-
Charging & Equalizing
Proper Torque Table
| Proper Torque Values for Connection Hardware | |||
| Flooded | VRLA | ||
| Automotive | 50 – 70 in-lbs | Button | 90 – 100 in-lbs |
| Side | 70 – 90 in-lbs | LT | 100 – 120 in-lbs |
| Wingnut | 95 – 105 in-lbs | ||
| LPT | 95 – 105 in-lbs | ||
| Stud | 120 – 180 in-lbs | ||
| LT | 100 – 120 in-lbs | ||
| WARNING: Use an insulated wrench when making battery connections. Do not overtighten terminals. Doing so can result in post breakage, post meltdown, or fire. | |||
Deep-cycle flooded/wet batteries need to be watered periodically. The frequency depends on battery usage, charging and operating temperature. Check new batteries every few weeks to determine the watering frequency for your application. It is normal for batteries to need more watering as they age.
Water should NEVER be added to deep-cycle AGM or gel batteries.
Trojan Battery Fill Chart
For Fully Charged Trojan Deep Cycle Batteries
Add water to 1/8" below bottom of the vent well.
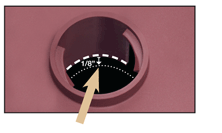
For Fully Charged Trojan Deep Cycle Batteries
Add water to the maximum water level indicator.

Water Impurity Limits
| Impurity | Parts Per Million | Effects of Impurity |
| Color | Clear and “White” | - |
| Suspended Matter | Trace | - |
| Total Solids | 100 | - |
| Organic and Volatile Matter | 50 | Corrosion of positive plate |
| Ammonia | 8 | Slight self-discharge of both plates |
| Antimony | 5 | Increased self-discharge, reduces life, lower on-charge voltage |
| Arsenic | 0.5 | Self-discharge, can form poisonous gas at negative plate |
| Calcium | 40 | Increase of positive plate shedding |
| Chloride | 5 | Loss of capacity in both plates, greater loss on the positive plate |
| Copper | 5 | Increased self-discharge, lower on-charge voltage |
| Iron | 3 | Increased self-discharge at both plates, lower on-charge voltage |
| Magnesium | 40 | Reduced life |
| Nickel | None Allowed | Substantial lowering of on-charge voltage |
| Nitrates | 10 | Increased sulfation on the negative plate |
| Nitrites | 5 | Corrosion of both plates, loss of capacity, reduced life |
| Platinum | None Allowed | Increased self-discharge, lower on-charge voltage |
| Selenium | 2 | Positive plate shedding |
| Zinc | 4 | Slight self-discharge of negative plate |
Check the battery for cleanliness at regular intervals and keep terminals and connectors free of corrosion. Terminal corrosion may adversely affect the performance of the battery and present a safety hazard.
Review the guide to Charging & Equalizing deep cycle batteries for a complete instructions.
Disclaimer: Information was derived from Trojan Battery and Trojan Battery User's Guides.


Login and Registration Form